Diagnostic accuracy is the foundation of quality dental care.
Every restoration, implant, and treatment plan depends on how precisely a condition is identified.
Yet, despite years of professional training, even the most experienced clinicians face challenges: subtle lesions can hide on radiographs, soft-tissue changes can go unnoticed, and interpretation errors can delay proper care.
The good news is that modern technology and structured workflows are dramatically improving diagnostic reliability.
1. Adopt High-Resolution Digital Imaging
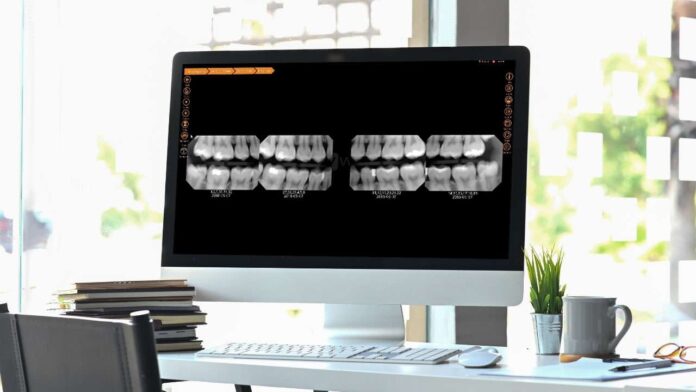
Switching from film-based X-rays to digital radiography remains one of the most impactful steps a practice can take.
Digital sensors produce sharper images with adjustable contrast and brightness, allowing clinicians to identify early caries, root fractures, or bone loss that might otherwise go undetected.
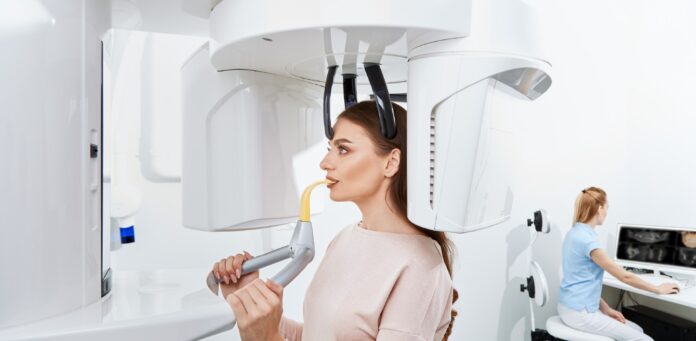
Beyond standard 2D imaging, cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) gives a true three-dimensional view of the oral cavity. CBCT is invaluable for endodontic evaluations, implant planning, and detecting periapical pathologies. It eliminates overlapping structures and enables cross-sectional analysis, helping clinicians visualize problems that traditional X-rays can miss.
Digital imaging also enhances collaboration. Images can be securely shared with specialists or stored for longitudinal comparison. Over time, this creates a full diagnostic history, allowing for better tracking of disease progression.
2. Integrate Artificial Intelligence for Second Opinions
AI has moved from theoretical to practical in dentistry. Systems trained on thousands of annotated scans can now analyze images in seconds, flagging anomalies that deserve a closer look.
For example, platforms such as Trust AI use machine learning to assist dentists in interpreting radiographs and CBCT scans. These tools identify patterns associated with caries, bone loss, or apical lesions, giving dentists an evidence-based “second opinion.”
The key is not automation, it’s augmentation. AI helps eliminate bias, reduce fatigue errors, and standardize diagnostic results across practitioners.
When combined with a dentist’s clinical judgment, these systems significantly raise accuracy rates. According to recent studies published in Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, AI-assisted diagnosis of periapical lesions achieved up to 92% accuracy, compared to 78–85% with human evaluation alone.
Incorporating AI into the workflow also improves patient communication. Showing a visual heatmap of AI-detected areas builds transparency and confidence; patients can see what the software and the clinician are identifying together.
3. Standardize Diagnostic Protocols
Consistency is a major driver of diagnostic accuracy. Implementing standard operating procedures (SOPs) ensures that each patient is examined under uniform criteria, reducing variability between practitioners.
For example, protocols might specify:
- When to use CBCT instead of panoramic imaging.
- How often to re-image specific cases (like periapical monitoring).
- Which indices to record for periodontal evaluations?
- Steps for documenting and reviewing radiographic findings.
By structuring diagnostics, practices eliminate guesswork and make decision-making reproducible. Pairing these protocols with digital templates in practice management software further reduces the chance of missing key findings.
4. Combine Clinical Data with Digital Models
Integrating intraoral scanners and 3D imaging allows for comprehensive visualization. Modern scanners can capture full-arch models in under two minutes, producing digital files accurate to within microns.
When merged with CBCT data, the result is a powerful diagnostic map showing both hard and soft tissue details.
This fusion is particularly valuable in implantology and orthodontics. It lets dentists simulate procedures, predict outcomes, and detect spatial conflicts before they become clinical problems.
Moreover, digital models are reusable; clinicians can overlay new scans months later to monitor changes, like bone remodeling or shifting tooth positions.
The real advantage lies in this repeatability: diagnostics become quantifiable over time rather than based on memory or manual notes.
5. Use Digital Workflows for Peer Review and Collaboration
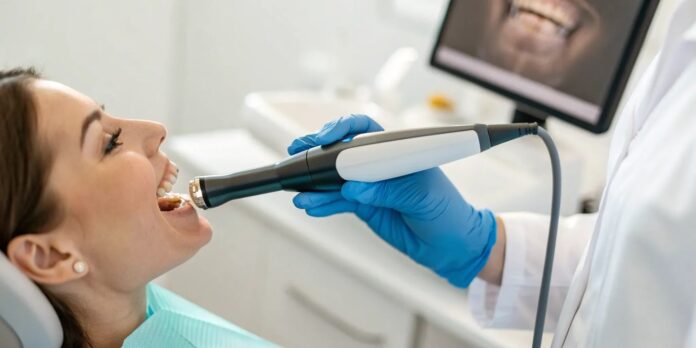
Even with modern imaging, human interpretation can still vary. That’s why digital ecosystems supporting remote collaboration are key. By sharing 3D scans, annotated X-rays, or AI-generated reports through secure cloud platforms, clinics can seek peer review without delay.
A second dentist across the country, or even an AI model integrated into a shared platform, can validate findings within minutes.
This kind of digital peer support is especially useful for complex cases like endodontic retreatments or pathologic lesions. It reinforces diagnostic reliability while maintaining efficiency.
Some clinics now integrate real-time collaboration directly into their imaging software, enabling virtual “case rooms” where multiple specialists can annotate and discuss findings synchronously.
6. Invest in Training for Digital Literacy
Technology only enhances accuracy if clinicians know how to use it effectively. Regular training in image interpretation, AI workflow integration, and data calibration ensures that digital tools serve as an extension of clinical reasoning rather than a replacement for it.
For instance, understanding how to adjust image contrast, detect motion artifacts in CBCT scans, or verify AI-generated results prevents overreliance on automation.
Workshops and continuing education courses focused on digital diagnostics now form part of the curriculum in leading dental associations.
Practices that train every team member, from hygienists to assistants, on these tools report fewer errors, faster image acquisition, and more consistent patient outcomes.
7. Prioritize Data Management and Calibration

Accurate diagnosis depends on data integrity. Poor calibration, incorrect exposure settings, or outdated software can distort imaging results. That’s why routine calibration of imaging devices and standardization of brightness and resolution across displays are non-negotiable.
Additionally, digital record management must be structured. Image tagging, secure backups, and consistent metadata make retrieval faster and reduce errors during follow-up visits. Over time, building a clean, searchable diagnostic archive enables trend analysis, identifying recurring issues or long-term treatment patterns.
8. Combine AI with Clinical Context
No matter how advanced, AI cannot interpret patient history, habits, or symptoms. True diagnostic accuracy comes when digital insight meets clinical context.
AI may flag bone loss, but only the dentist can connect it to systemic conditions like diabetes or smoking history.
That balance between human reasoning and computational analysis defines the next phase of precision dentistry.
9. Monitor and Audit Diagnostic Outcomes
Finally, improving accuracy means measuring it. Practices should establish regular diagnostic audits, comparing outcomes with predictions. For example:
- Were AI or imaging-based findings confirmed during treatment?
- Did early interventions prevent more serious complications?
- Are false positives or negatives trending in a specific direction?
Auditing not only refines internal processes but also drives continuous improvement. When combined with feedback from AI systems, it creates a learning loop that strengthens diagnostic performance over time.
Bottom Line
Within the next decade, digital dentistry will become even more predictive. Imaging systems will integrate with patient biometrics, saliva testing, and genetic data to forecast disease susceptibility.
AI tools will deliver real-time, chairside analysis, alerting clinicians before pathology becomes visible.
Yet, amid all the innovation, the defining factor remains human expertise. Digital systems amplify what skilled dentists can already do: observe patterns, interpret context, and make informed decisions.
Technology doesn’t replace clinical intelligence; instead, it magnifies it.
Modern practices that merge imaging, AI, and structured workflows aren’t just diagnosing better; they’re reshaping the meaning of precision care.
The result is fewer missed lesions, faster treatments, and patients who understand their oral health more clearly than ever before.